Identity is one of the most important aspects of our daily lives both online and offline.
An identity can has be seen as a set of properties we assign to an individual. Properties can be biometric (how we look), geospatial (country) or historic.
Governments and legal identities issue certificates about our identity. A typical example is a passport.
A passport is technically a proof, that you physically went to a government office with a copy of your birth certificate and your photo and you provided the information to a trusted employee. The government would then issue a passport certifying that information in the passport is bound to a set of biometric properties, our photo and (in new passports) finger prints or retina scan.
The passport representes three claims.
- Your birth certificate.
- Your visual appearance and other biometric properties like (finger prints and retina scan.
- Residency in a specific country.
An identity boils down to a collections of claims. A claim can be used to generate another claim linking them together. I can use an id card to apply for a driving license. The claim in the id card will allow me to generate a new claim with is my driving license,
It is important to note that claims can be revoked. My driving license can be revoked but my identity card can still be valid.
The main issue of the current identity mechanisms is that the user does not own his personal information. Information in centrally stored by the government institutions and you don’t have control of when information about your identity is accessed.
The Ethereum blockchain provides the perfect platform to improve the issue and management of identities. Currently there are two main standards that tackle identity management, ERC 725 and ERC 735. They are the brainchild of Fabian Vogelsteller which among of many things is the creator of the ERC20 token standard.
Following the success of ERC 20 with ICOs. Fabian wants to design a standard that can be used to build identity management systems. As with ERC 20, these ERCs comes with the data structure of the subject, and the functions (interfaces only, without actual implementation) and events on the identity.
ERC 725 is a standard for publishing and managing an identity via a smart contact. These identity smart contracts can be used to describe humans, machines are any object or group. ERC 735 is an associated standard to add and remove claims to an ERC 725 identity smart contract.
In ERC 725 an identity is represented by a smart contact. The smart contract has three main components.
Keys
Are the main actors and are as used for login or access, to make transactions, sign documents or sign claims for other identities .
Execution
Execution is about acting as your identity, executing contracts, voting etc and also having the possibility to add claims to other identities and contracts.
Claims
Claims is a statement that an entity makes about another entity. A claim can be added by anyone but requires approval from the owner of the smart contract. Changes to the claim also requires permission by the owner of the smart contact. Claims can be removed by the issuer and the owner of the smart contract.
If your smart contact contains a driving license signed by a Transport authority. The transport authority can remove the claim that you have a valid driving license if you have been a bad driver and didn’t obey the rules.
The claim contains the issuer signature and a reference to the actual claim which can be a hash or a bit-mask. The data is not present in the blockchain but rather just a reference.
This is particularly important if the data is sensitive like your medical records. A doctor can add a claim that a patient suffers from from a particular illness. This gives the owner of the smart contract to possibility to get medication from a pharmacy based on his claim. However details about his condition are not disclosed on the blockchain. The blockchain only contains a reference to the data.
In the scenario someone requires access to the data. The owner of the data is still under control as the data can be encrypted with both the signature of the issuer and the owner of the smart contract. If a doctor needs access to your medical claims, You can provide permission by decrypting the information with your private key and the information the provided to the entity requesting the information.
The nice thing about this standard is the segregation of identities and claims which are handles in two different standards. It also covers scenarios were properties of our identity change. eg sex, marriage status, etc. All these can be separate claims which can be added or removed.
How will it work in the real world ?
Your identity is simply the address of the smart contract on the blockchain and the ownership of the keys (public private) present in the contract. Having the private keys allows us to proof ownership of the smart contract.
The identity can be used both off-chain and on-chain.
A typical off-chain scenario were you are requesting to physical access to a building.

Assuming the security guard has a mobile device. He can send a random string to my mobile device. I can append the address of the my identity contact and sign both pieces of information using my private key. The guard receives the information and can validate that.
- I am the owner of the smart contract.
- He can check the validity of the claim that I can access the building by checking the issuer that signed the claim.
On-chain scenario requires less steps.
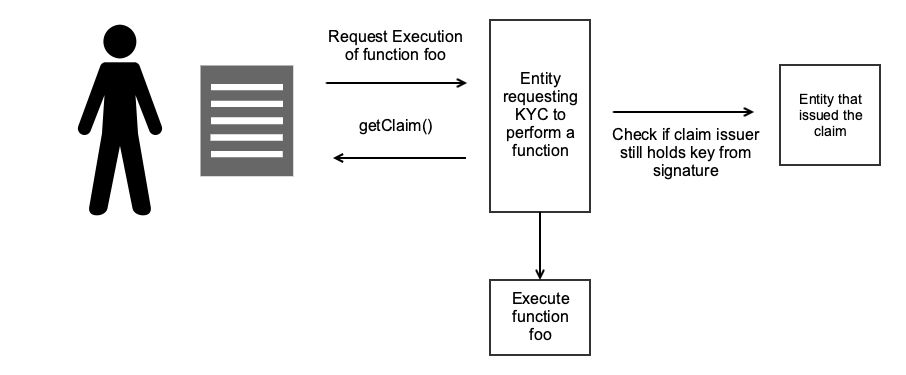
Let say i want to execute a smart contract, Now this smart contract requires KYC to execute the function. The smart contract can request the claims present in my identity (smart contract) and validate that the issuer of the that signed the claim. If all checks ok the smart contract will execute the function I requested.
The nice part of these two standards if that they provide a basic framework that define basic rules which can be extended to incorporate any scenario both off-chain and on-chain. Work on this protocol has now been merged as an alliance between individuals and organisations working on the blockchain to standardise the creation and use of identities on the blockchain.
Hope you liked this article. Feel free to add me on Linkedin here or contact me on email on [email protected].


